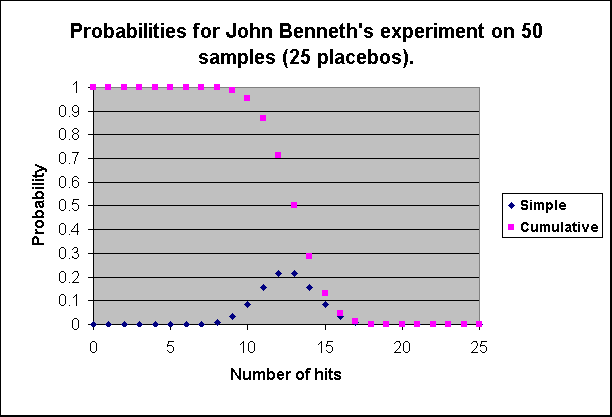
| This is a statistical analysis of John Benneth's experiment on 50 samples (25 placebos) as described at http://www.marius.net/protocol.html . The simple probability refers to the chance of getting exactly n positive hits by random guessing. It is calculated using Excel's hypergeometric function. The cumulative probabability refers to the chance of getting at least n hits and is obtained by summing simple probabilities from n to 25. The numerical error is of the order of 1.0E-09, i.e one chance in a billion. | ||
| Number of hits | Simple probability | Cumulative probability |
| 0 | 7.91073E-15 | 1 |
| 1 | 4.94421E-12 | 1 |
| 2 | 7.11966E-10 | 1 |
| 3 | 4.18478E-08 | 0.999999999 |
| 4 | 1.26589E-06 | 0.999999957 |
| 5 | 2.23304E-05 | 0.999998692 |
| 6 | 0.000248115 | 0.999976361 |
| 7 | 0.001827952 | 0.999728246 |
| 8 | 0.009254006 | 0.997900294 |
| 9 | 0.033017379 | 0.988646288 |
| 10 | 0.084524489 | 0.95562891 |
| 11 | 0.157173637 | 0.871104421 |
| 12 | 0.213930784 | 0.713930784 |
| 13 | 0.213930784 | 0.5 |
| 14 | 0.157173637 | 0.286069216 |
| 15 | 0.084524489 | 0.128895579 |
| 16 | 0.033017379 | 0.04437109 |
| 17 | 0.009254006 | 0.011353712 |
| 18 | 0.001827952 | 0.002099706 |
| 19 | 0.000248115 | 0.000271754 |
| 20 | 2.23304E-05 | 2.36388E-05 |
| 21 | 1.26589E-06 | 1.30846E-06 |
| 22 | 4.18478E-08 | 4.25647E-08 |
| 23 | 7.11966E-10 | 7.16918E-10 |
| 24 | 4.94421E-12 | 4.95212E-12 |
| 25 | 7.91073E-15 | 7.91073E-15 |

E-Mail: feedback@weirdtech.com